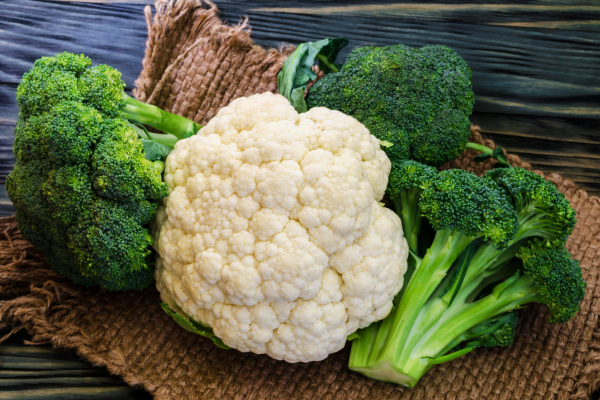
Cauliflower and broccoli are from the same family Brassicaceae also known as the Cruciferae. They both are well-known for their versatility in the kitchen and their nutritional benefits. However, which one is healthier remains debatable.
In this blog, we will understand the nutritional profiles, health benefits and other benefits.
Nutritional profile
The table will show the difference in the nutritional values of cauliflower and broccoli.
| Nutritional Profile | Broccoli | Cauliflower |
| Water | 89.3 g | 92.1 g |
| Energy | 34 Kcal | 25 Kcal |
| Protein | 2.82 g | 1.92 g |
| Total lipid | 0.37 g | 0.28 g |
| Carbohydrate | 6.64 g | 4.97 g |
| Total dietary fibre | 2.6 g | 2 g |
| Total sugar | 1.7 g | 1.91 g |
| Vitamin C | 89.2 mg | 48.2 mg |
| Thiamin | 0.071 mg | 0.05 mg |
| Riboflavin | 0.117 mg | 0.06 mg |
| Niacin | 0.639 mg | 0.507 mg |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.573 mg | 0.667 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.175 mg | 0.184 mg |
| Folate | 63 mcg | 57 mcg |
| Vitamin A | 623 IU | 0 IU |
| Vitamin E | 0.78 mg | 0.08 mg |
| Vitamin K (phylloquinone) | 102 mcg | 15.5 mcg |
| Calcium | 47 mg | 22 mg |
| Iron | 0.73 mg | 0.42 mg |
| Magnesium | 21 mg | 15 mg |
| Phosphorus | 66 mg | 44 mg |
| Potassium | 316 mg | 299 mg |
| Sodium | 33 mg | 30 mg |
| Zinc | 0.41 mg | 0.27 mg |
| Copper | 0.049 mg | 0.039 mg |
| Manganese | 0.21 mg | 0.155 mg |
| Selenium | 2.5 | 0.6 mcg |
Bioactive compounds
Broccoli
The bioactive compounds found in broccoli are sulphoraphane, indole-3-carbinol, isothiocyanates, flavonoids and quercetin. These compounds have anti-inflammatory and high antioxidant properties, which help reduce the risk of developing any chronic diseases and inflammation in the body.
Cauliflower
Phytochemicals, hydroxycinnamic, caffeic, chlorogenic, ferulic, and synaptic acids, flavonoids, quercetin and anthocyanins are the bioactive compounds found in cauliflower. Studies showed that different cooking methods have different effects on these compounds.
Digestive health
Comparing the two, broccoli has a slightly higher fibre content than cauliflower. But both feed gut bacteria and promote healthy gut microbiomes.
Weight management
Both are low in calories and have good fibre content. For losing weight, they are a wise option. They offer a wide range of benefits, improving satiety and thereby reducing overeating.
Other benefits
Broccoli is high in vitamin A, calcium and vitamin K. These promote good eye health and bone health.
From the above comparison, we can understand that broccoli is high in all the nutrients when compared to cauliflower. But it does not mean that cauliflower is not a good vegetable. Broccoli and cauliflower are not native to all the countries and also it is not easily available everywhere. When it is not native to a country the product is either imported or genetically cultivated.
Vegetables are perishable products, they can lose nutrients during importation due to long travel hours, might get spoiled due to improper maintenance of temperature and many other reasons. Genetically modified crops may potentially cause new allergic reactions and contribute to antibiotic resistance. This can cause many adverse effects on the body.
Consuming a vegetable that is native to the place will provide all the necessary benefits that are required. They are also cost-effective and easily available, unlike imported vegetables.
In India, cauliflower is native to the country; it is also cost-effective and easily available. Broccoli, on the other hand, is imported or cultivated in hill stations under greenhouses, which may result in fewer nutrients compared to natively grown broccoli.
To conclude, broccoli and cauliflower are healthy and have health benefits. Eating a vegetable that is native to its place will provide all the benefits one needs.
Kripa N,
Senior Clinical Dietitian, Simplyweight