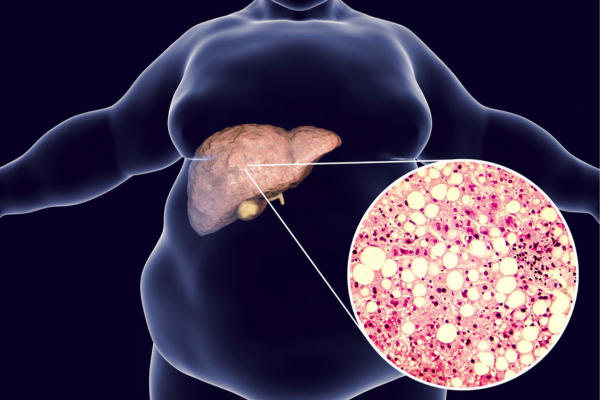
The liver is located at the upper right side of the abdomen. It is the largest internal organ of the human body. The main function of the liver is to remove toxins from the body and process food and nutrients. Hepatic steatosis is an alternative term for fatty liver. It takes place when the liver accumulates fat. While a small amount of fat in the liver is healthy, too much fat can have negative health effects. The body needs good fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids, to function properly. Numerous studies have been carried out to investigate its nature and its therapeutic benefits for a range of illnesses.
This essential nutrient is not produced by the body in adequate amounts. As a result, in order to benefit from omega 3, we must consume foods high in them, such as fish and supplements.
Fatty liver disease
The second-largest organ in the body is the liver. It assists in obtaining nutrients from meals and beverages and removes toxins from your blood.
An excessive amount of fat in the liver can lead to inflammation, which can harm and scar the liver. Liver failure may result from this scarring in extreme circumstances.
Alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) is the term used to describe fatty liver that occurs in heavy alcohol users.
It is referred to as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in individuals who do not use large amounts of alcohol.
What are the symptoms of fatty liver?
Simple fatty liver – Excess fat has accumulated in the liver. If a simple fatty liver does not worsen, it is often normal.
Steato hepatitis – There is inflammation in the liver in addition to additional fat.
Fibrosis – The liver’s chronic inflammation has now resulted in scarring. The liver continues to function normally in most cases, though.
Cirrhosis – The liver’s capacity to function is compromised by widespread liver scarring. This is the most serious phase, and it cannot be reversed.
What foods should be avoided?
- Sugar-filled drinks such as sports drinks, juice, soda, and lemonade have to be stayed away from.
- One should restrict their intake of red meats, cold cuts, bacon, and other processed meats.
- Butter intake should also be limited, and trans fats like fried foods, such as french fries, fried chicken, and doughnuts, processed snacks, such as crackers and chips and baked goods should be avoided completely.
Tips to be followed
- Concentrate on eating a plant-based, whole-foods diet – Make sure your diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and legumes. These foods can be helpful for people with fatty liver disease since they are low in trans and saturated fats and high in fibre, vitamins, and minerals.
- Fast food, snacks, and baked goods are examples of processed foods that frequently include high sugar, bad fats, and additives that aggravate fatty liver disease.
- Processed meals can increase the amount of fat accumulated in the liver and cause inflammation in the liver because they frequently contain high levels of fructose, harmful fats like trans and saturated fats, and additives.
- Avoid red meats and processed meats, which are heavy in saturated fats, and choose lean protein sources instead, such as skinless chicken, fish, beans, and lentils. These foods provide a lot of fibre, iron, and protein.
- Sports drinks, soda, juice, and lemonade are examples of sugary drinks that might hasten the onset of fatty liver disease. Carbonated and sugary drinks are high in fructose and other sugars. Excessive consumption of these sugars causes the liver to digest them and turn them into fat, which causes the fat to build up in the liver cells. Choose water, coffee, or unsweetened tea instead.
- Eating too much can induce weight gain and increase your chance of getting fatty liver disease, so be mindful of how much you consume. To help you regulate your portion sizes, use smaller cups or dishes. Be mindful of how much you eat at each meal.
- Limit your alcohol intake because too much of it can harm your liver and make fatty liver disease worse. If you decide to drink, always check with your healthcare practitioner first and in moderation. Notably, the American Liver Foundation advises total abstinence from alcohol, particularly for people suffering from alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Fatty acids
Carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen make up fatty acids. There are two different kinds of fatty acids: unsaturated and saturated. It is possible to further divide unsaturated fats into polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats.
Because they increase the risk of heart disease and stroke, saturated fats are sometimes referred to as “unhealthy fats.” Conversely, when utilised in moderation, unsaturated fats also known as “healthy fats”support heart health. Polyunsaturated fat is what the omega 3 is categorised as.
Types of omega-3
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are the three forms of Omega-3 fatty acids. Because ALA is found in plants while EPA and DHA are found in fish, these fatty acids are known as marine omega-3s.
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is slightly converted by our body into docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). Omega 3 is essential for healthy cell membranes, which has an impact on your body’s general health.
Side effects of omega 3
Marine foods are an excellent and convenient source of omega-3. However, certain fish are higher in mercury than others. It may therefore be toxic and raises the possibility of a high concentration of mercury in our food.
Fish like shark, swordfish, orange roughly, marlin, king mackerel, and others have high mercury levels. Before taking omega supplements, always see your doctor as they may have special advice and cautions.
Conclusion
The most effective treatment for NAFLD is weight loss attained by a healthy eating pattern and increased physical exercise. Enhancing food quality and increasing physical activity both lower the chance of CVD incidence and NAFLD advancement. It is challenging to alter one’s lifestyle in an obesogenic atmosphere, yet even little advancements have an impact. Health care professionals are essential in helping their patients succeed in the long run.
Nesha Felciya,
Clinical Dietitian, Simplyweight